Your blood plays a vital role in keeping you alive and healthy. It delivers oxygen to cells, fights off infections, and seals up injuries to prevent excessive bleeding. Part of this process is clotting, where your blood forms clots to stop leaks in blood vessels. While clotting is essential, sometimes it happens when or where it’s not supposed to, leading to blood clotting disorders. These conditions can have serious consequences for your health, from blocking blood flow to vital organs to increasing the risk of strokes or heart attacks.
But how can you tell if something is wrong with your blood’s clotting process? Recognizing the early warning signs of blood clotting disorders can help you seek treatment early and prevent further complications. This guide will explain what blood clotting disorders are, their early symptoms, potential causes, and what you can do to maintain healthy blood circulation.
What Are Blood Clotting Disorders?
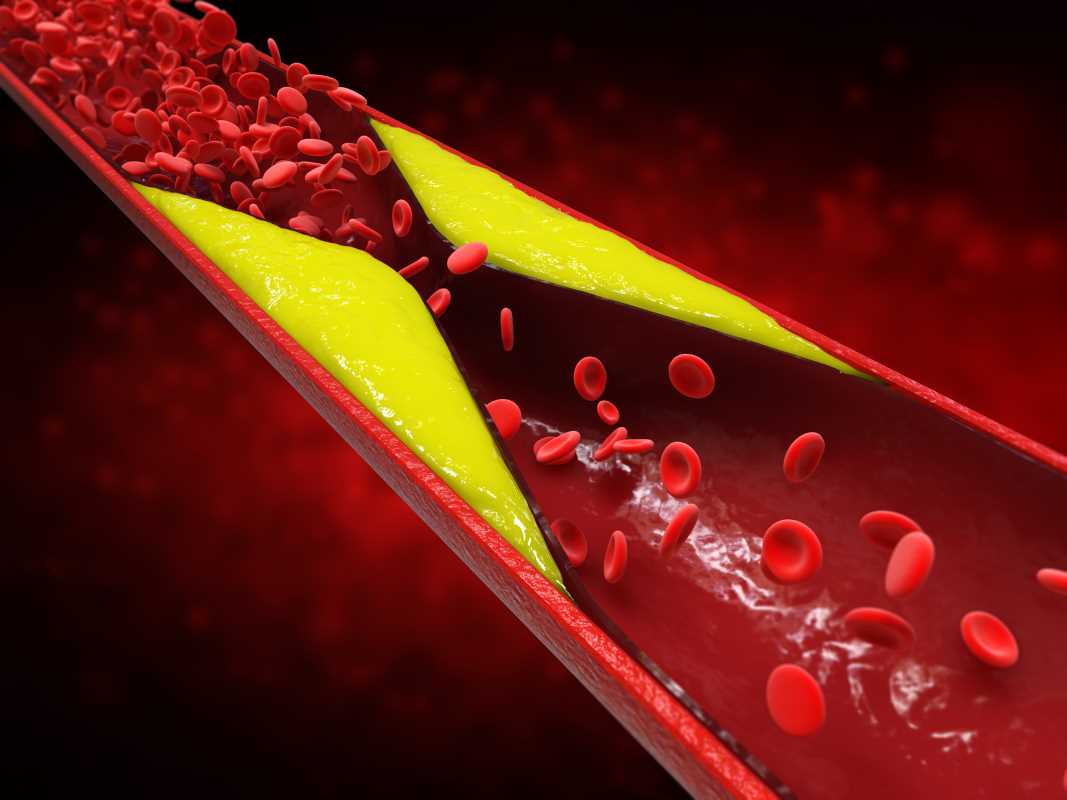
Blood clotting, or coagulation, is a natural process that prevents bleeding when you have an injury. Special blood cells called platelets, along with proteins in your plasma, work to form a “plug” at the site of the injury.
However, a blood clotting disorder occurs when this process goes haywire. Sometimes your blood clots excessively, leading to blockages in your veins or arteries. Other times, your blood may not clot enough, leaving you vulnerable to uncontrolled bleeding. Both scenarios can be dangerous.
Common blood clotting disorders include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A clot that forms deep in a vein, often in the legs.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A serious condition where a clot travels to the lungs.
- Hemophilia: A disorder where the blood doesn’t clot properly, leading to excessive bleeding.
- Thrombophilia: A tendency for your blood to clot too easily due to genetic or acquired factors.
- Knowing the early signs of these disorders can save lives, as complications from abnormal clotting can develop quickly and severely.
Early Warning Signs of Blood Clotting Disorders
Spotting a blood clotting disorder early is crucial because untreated clots can cause significant damage. Here are the common warning signs to watch for.
1. Swelling in One Area
If you notice swelling in one leg, arm, or other part of your body, it could be due to a blood clot blocking blood flow. This is often seen in DVT. The swelling may come with warmth or tenderness in the affected area.
2. Redness or Discoloration
Unexplained redness or purple discoloration, especially on your legs, might indicate a blood clot. This discoloration happens because blood pools behind the clot, overwhelming your veins.
3. Pain or Tenderness
Sharp, cramping pain or soreness in a specific area, like your calf or thigh, could signal a blood clot. This pain might worsen when you stand, walk, or touch the affected spot.
4. Shortness of Breath
If you suddenly feel like you can’t catch your breath or experience a sharp chest pain, this could be a sign of a pulmonary embolism. A clot blocking blood flow to the lungs is an emergency and requires immediate medical attention.
5. Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding
For women, heavy periods that last longer than normal might indicate a clotting issue. This is especially concerning if it’s paired with easy bruising or frequent nosebleeds.
6. Unexplained Bruising
Do you bruise easily or notice large, dark bruises without any clear cause? This can be an early sign of a platelet issue or a bleeding disorder like hemophilia.
7. Warmth in One Area
If part of your body feels warm to the touch, especially in a swollen leg or arm, this could signal a clot causing inflammation.
8. Sudden, Persistent Headaches
Migraines or severe headaches that come out of nowhere and don’t respond to usual treatments might point to a clot in the brain. This is rare but serious.
Potential Causes of Blood Clotting Disorders
What leads to a blood clotting disorder? There’s no single answer, as these conditions can be caused by a mix of genetic, lifestyle, and medical factors.
1. Genetic Factors
Some people inherit conditions like Factor V Leiden or prothrombin gene mutations, which increase their risk for developing abnormal clots.
2. Prolonged Immobility
Sitting still for long periods, like during a long flight, a hospital stay, or desk work, slows blood flow, making clots more likely.
3. Surgery or Injury
Trauma to blood vessels or surgery triggers your natural clotting response, which can sometimes go into overdrive.
4. Medications
Certain medications, like birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, or chemotherapy, can increase clotting risks.
5. Other Medical Conditions
Conditions like obesity, diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases can raise your risk for blood clotting disorders.
6. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, dehydration, and high blood pressure add to your risk. Smoking damages blood vessels, while dehydration thickens your blood, making clots more likely.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While minor discomfort might not always mean a clotting disorder, some symptoms are too serious to ignore. You should seek medical care immediately if you experience:
- Sudden, unexplained shortness of breath.
- Swelling, redness, or warmth in one leg or arm.
- Severe chest pain that feels sharp or radiates to your arm or back.
- Persistent headaches paired with vision problems or trouble speaking.
- Heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop, like nosebleeds or prolonged menstrual periods.
- Early treatment can prevent further complications like stroke or organ damage, so don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional.
Tips for Prevention and Maintaining Healthy Blood Circulation
The good news is that there are steps you can take to lower your risk of blood clotting disorders and keep your circulatory system healthy.
1. Stay Active
Walking, stretching, and avoiding long periods of sitting can help blood flow freely. If you’re on a long flight or stuck at a desk job, make a point to move every hour.
2. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can thicken your blood, increasing your risk of clots. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day keeps your blood flowing smoothly.
3. Eat a Healthy Diet
Focus on foods that promote heart and blood vessel health, such as:
- Leafy greens (rich in vitamin K).
- Fatty fish (high in omega-3s).
- Fruits like berries and oranges (full of antioxidants).
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking damages your blood vessels and encourages clot formation. Quitting is one of the best things you can do for your overall health.
5. Wear Compression Stockings
If you’re at a higher risk of clots, compression socks can improve blood flow in your legs and reduce swelling.
6. Manage Chronic Conditions
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or another chronic condition, keeping it under control can reduce your clotting risk.
7. Know Your Family History
If clotting disorders run in your family, talk to your doctor about your risks. They may recommend testing or preventative strategies like blood thinners.
 (Image via
(Image via