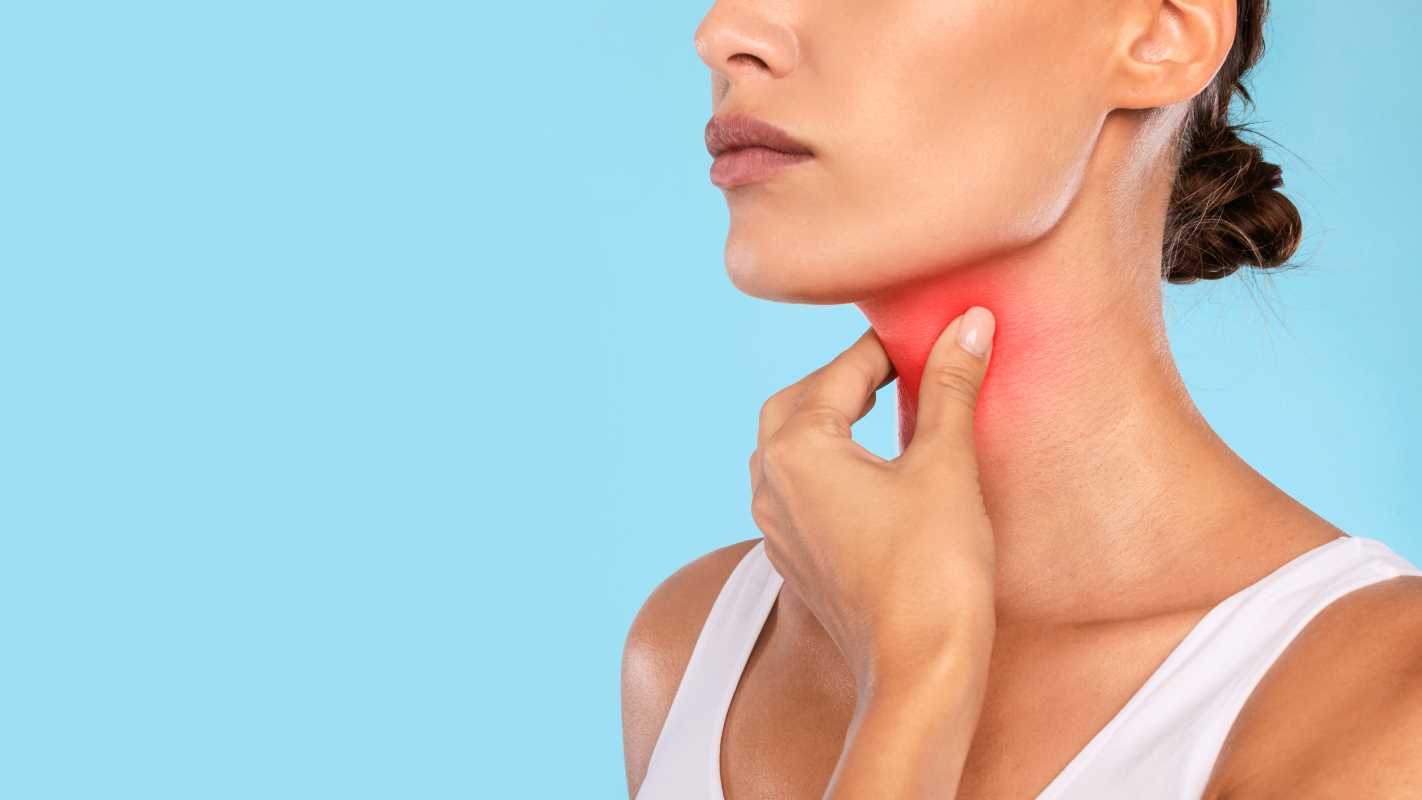
Feeling tired, gaining weight, or dealing with unexplained mood changes? These could just be signs of a busy life, but they might also point to something more specific happening in your body. Your thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck, plays a vital role in regulating how your body works. When something goes wrong with your thyroid, the effects can show up in surprising ways.
Thyroid disorders are incredibly common, affecting millions of people worldwide. The good news? Many symptoms are treatable once the condition is identified. This guide will help you recognize the signs of thyroid disorders, understand how the gland works, and know when it’s time to see a doctor.
What Does the Thyroid Do?
Your thyroid gland is small but mighty. Located at the front of your neck just below the Adam’s apple, this gland produces hormones that help control several important bodily functions, including:
- Metabolism: How your body converts food into energy.
- Heart Rate: Regulating how quickly (or slowly) your heart beats.
- Temperature Regulation: Helping maintain a stable body temperature.
- Growth and Development: Especially during childhood and adolescence.
- Mood and Energy Levels: A critical function in your emotional well-being.
The thyroid produces two main hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): The primary hormone, which your body converts into the active form.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): The active form, which directly affects how your cells function.
When the thyroid produces too much or too little of these hormones, the delicate balance of your body gets disrupted.
Common Types of Thyroid Disorders
Before we jump into the symptoms, it’s helpful to understand the two main categories of thyroid disorders:
- Hypothyroidism: The thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones, slowing things down in your body.
- Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid makes too many hormones, speeding things up.
Other conditions like thyroid nodules, goiters, Hashimoto’s disease, or thyroid cancer can also impact the gland, but hypo- and hyperthyroidism are the most common.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, often develops slowly and can be hard to recognize at first. It’s more common in women, especially those over age 60. Here are the most common signs:
1. Fatigue
If you’re always feeling tired no matter how much you rest, your thyroid could be to blame. Low hormone levels slow your body down, leaving you constantly drained.
2. Weight Gain
Unexplained weight gain is a red flag for hypothyroidism because your metabolism slows down when the gland isn’t producing enough hormones.
3. Cold Intolerance
Feeling cold when others are comfortable? An underactive thyroid can make it hard for your body to regulate temperature.
4. Dry Skin and Hair
Hypothyroidism can lead to dry, flaky skin and brittle hair or nails since these tissues rely on a healthy metabolism to stay strong and nourished.
5. Constipation
Digestive processes slow down with low thyroid hormones, making constipation a frequent symptom.
6. Depression or Mood Changes
Low thyroid levels can significantly impact your mood, leading to feelings of sadness, depression, or anxiety.
7. Muscle Weakness or Joint Pain
A sluggish thyroid can cause muscle cramps or joint aches that seem to come out of nowhere.
8. Puffy Face
Swelling in the face, particularly around the eyes, is another common but less-recognized symptom.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, speeds up your body’s processes. This condition is often caused by Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder. Here’s what to watch for:
1. Unexplained Weight Loss
Even if you’re eating normally, an overactive thyroid can cause dramatic weight loss because your metabolism is in overdrive.
2. Anxiety or Restlessness
Many people with hyperthyroidism report feeling anxious, jittery, or unable to relax—even in calm situations.
3. Rapid Heartbeat or Palpitations
Your heart works harder with overactive thyroid hormones, leading to a faster pulse or uncomfortable heart palpitations.
4. Sweating or Heat Intolerance
If you’re constantly sweating or feeling overheated compared to others, it could be a sign of an overactive thyroid.
5. Tremors
You might notice a mild shaking in your hands or fingers due to increased nervous system activity.
6. Frequent Bowel Movements
An overactive thyroid often speeds up digestion, leading to diarrhea or more frequent trips to the bathroom.
7. Bulging Eyes
A tell-tale sign of Graves’ disease, bulging eyes happen when the tissues around the eyes swell.
8. Difficulty Sleeping
Hyperthyroidism can make it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep, leaving you feeling exhausted during the day despite your body being in overdrive at night.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing any combination of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. Thyroid disorders are diagnosed through:
- Physical Exams: Your doctor may check for swelling or lumps around your neck.
- Blood Tests: A thyroid panel measures levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3, and T4 in the bloodstream.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds or scans may be used to examine the gland more closely.
Early detection is key since untreated thyroid problems can lead to complications like heart disease, infertility, or long-term damage to the gland.
How Thyroid Disorders Are Treated
Fortunately, thyroid disorders are highly treatable, and most people see significant improvements with proper care. Treatment depends on the condition:
- Hypothyroidism: Typically managed with daily thyroid hormone replacement medication like levothyroxine.
- Hyperthyroidism: May involve antithyroid medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to reduce hormone production.
- Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet with iodine-rich foods (like seaweed, fish, or dairy) can support thyroid health.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress, sleeping well, and maintaining a healthy weight are also important.
Small Changes Can Make a Big Difference
If your thyroid is out of balance, the symptoms might feel overwhelming. But it’s crucial to remember that there’s help available. With the right treatment plan and some lifestyle adjustments, most people can manage their symptoms and live full, healthy lives.
Keep an eye on how you feel, and don’t hesitate to ask your doctor for a thyroid evaluation if something seems off. Your thyroid might be small, but its impact on your overall health is huge. Taking care of it means taking care of you!
 (Image via
(Image via